Marine Animals Definition Biology

Marine biology is the scientific study of plants and animals that live in salt water.
Marine animals definition biology. Marine environments are therefore the most common habitat on Earth. Osculum- large opening that lets water out. When we talk about marine life the first thing that is likely to come to your mind is various species of fish.
Name the three body forms of sponges and define. Spongin- flexible protein fibers. Not only that but water provides a 3-dimensional habitat which increases the available habitat for the animals microbes and plants to live.
It also deals with airborne and terrestrial organisms that depend directly upon bodies of salt water for food and other necessities of life. Spicules- skeletal elements that support a sponge. An animal belonging to the mammalian order Sirenia which includes manatees and dugongs.
This type of pollution occurs when human activities notably the use of fertilizer on farms lead. Earth is often referred to as the blue planet because seas and oceans cover more than 75 of the Earths surface. So a marine biologist studies.
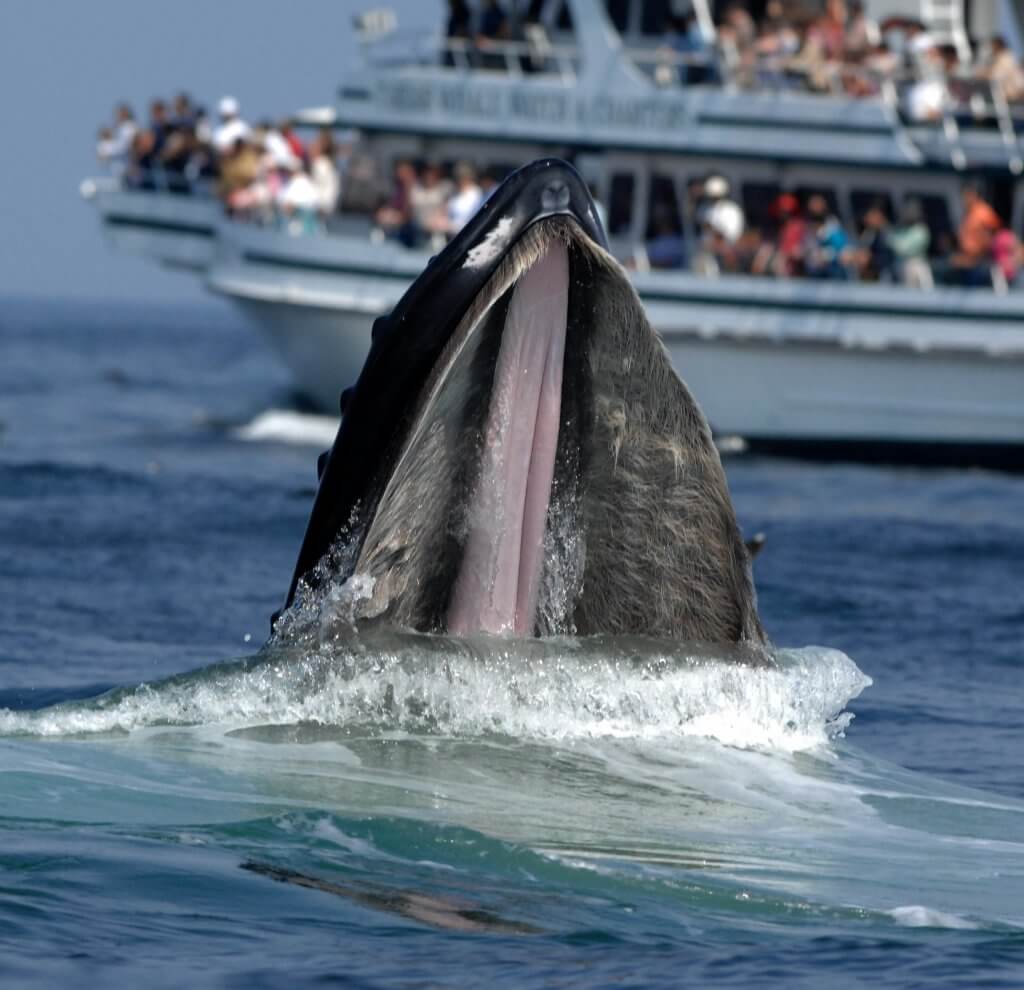
Archaeocytes- cells that move through the sponge. These organisms take many forms from the tiniest single-celled plankton to the largest animal on Earth the blue whale. What is Marine Biology.
Spongocoel- spacious cavity in sponge. Marine biology the science that deals with animals and plants that live in the sea. The study of marine life is called marine biology and a person that studies marine life is called a marine biologist.