Cellular Respiration Meaning In Biology

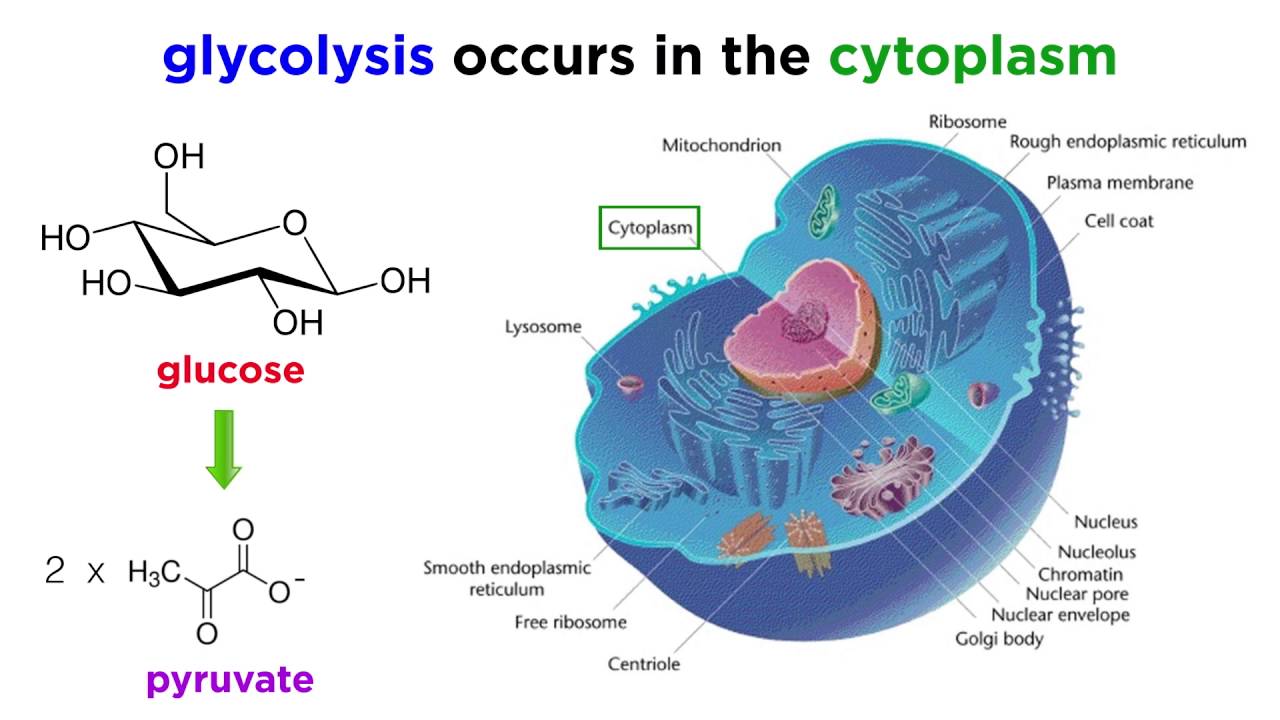
The process takes place in the cytoplasm of a cell.
Cellular respiration meaning in biology. Cellular respiration biology definition. Related Biology Terms. A series of metabolic processes that take place within a cell in which the biochemical energy is harvested from an organic substance eg.
Other types of organisms such as animals fungi many protozoa and a large. Based on the oxygen demand cellular respiration is divided into- Aerobic respiration and Anaerobic respiration. In contrast to simple combustion cellular respiration involves the step-wise release of energy in a tightly regulated fashion.
Cellular respiration is a process that all living things use to convert glucose into energy. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate ATP and then release waste products. Anaerobic respiration is another type of cellular respiration that takes place in the absence of oxygen and produces energy.
But cellular respiration is slightly more complicated than just converting the energy from glucose into ATP. Some organisms such as plants can trap the energy in sunlight through photosynthesis see Chapter 5 and store it in the chemical bonds of carbohydrate molecules. Introduction to Cellular Respiration.
Cellular respiration refers to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration but is often synonymous with aerobic respiration. Autotrophs like plants produce glucose during photosynthesis. Cellular respiration is the set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate and then release waste products.
Aerobic respiration requires oxygen to fully oxidise the organic molecule. Cellular respiration is a biological process in which cells convert sugar amino acids and fatty acids into energy utilized by the cell. Cellular respiration can be described as the reverse or opposite of photosynthesis.