Cellular Respiration Equation Definition

The simplified formula for aerobic cellular respiration is.
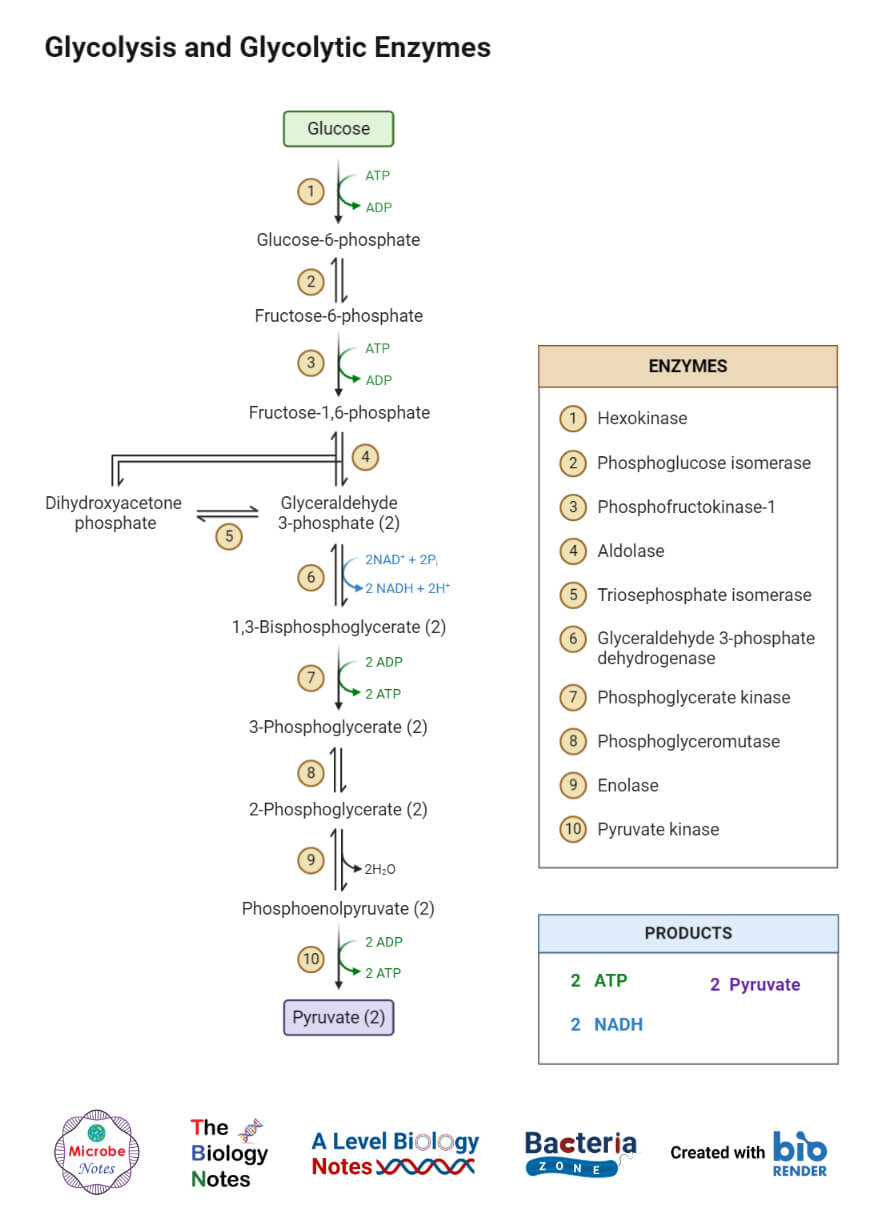
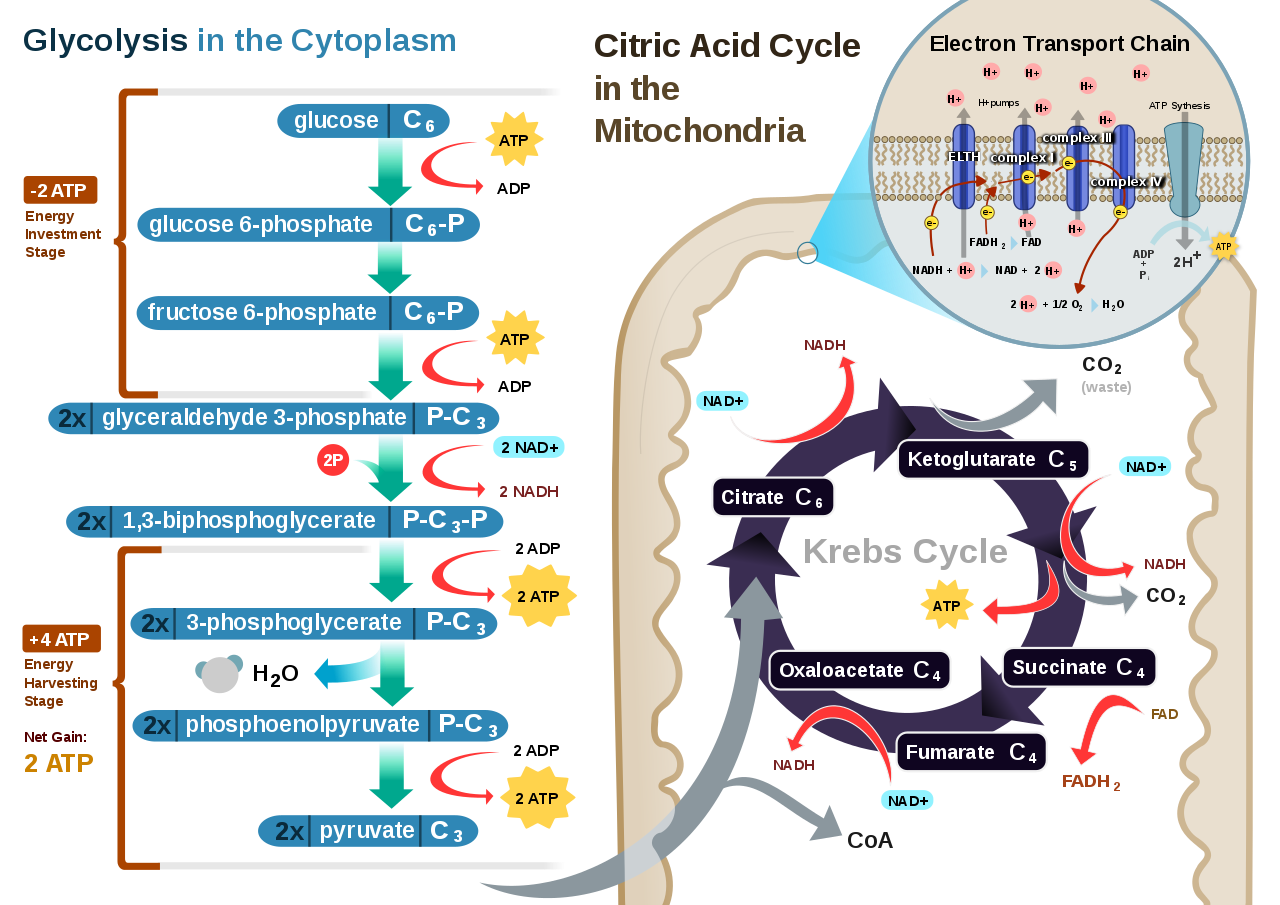
Cellular respiration equation definition. It is a continuous process that takes place within the cells of animals and plants. The reactions involved in cellular respiration are catabolic reactions that involve the breakdown of larger organic molecules into smaller forms. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic processes.
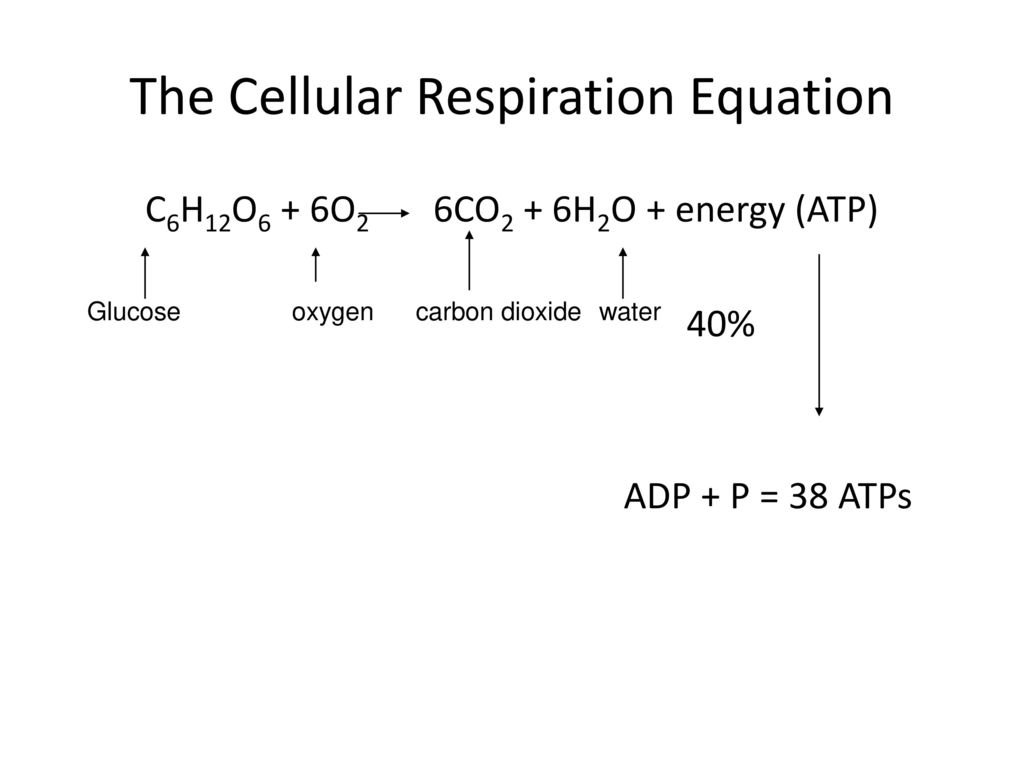
What is Cellular Respiration Definition Facts types 2. It is also known as a catabolic reaction as a large molecule like a carbohydrate is broken down into smaller molecules. Cellular Respiration aerobic C6H12O6 6O2 6CO2 6H2O 32 ATP Photosynthesis 6CO2 6H2O C6H12O6 6O2 By looking at the two formulas it becomes evident that the products of one of the reactions are reactants of the other.
Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate ATP and then release waste products. Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into energy. The cellular respiration equation is a part of metabolic pathway that breaks down complex carbohydrates.
Aerobic or respiration in the presence of oxygen and anaerobic or respiration without oxygen. This process can be explained with the help of the chemical equation. Its overall chemical reaction of cellular respiration equation is simplified as.
Glucose sugar Oxygen Carbon dioxide Water Energy as ATP Cellular respiration is the process of breaking sugar into a form that the cell can use as energy. The following are general representations formulae for both photosynthesis and cellular respiration. C 6 H 12 O 6 6 O 2 6 CO 2 6 H 2 O 38ATP Glucose 6.
Definition an organelle in eukaryotic cells that is the site of cellular respiration and generates most of the cells atp nucleus definition an organelle in a cell that holds the cells dna plural. The word equation for cellular respiration is. It is an exergonic reaction where high-energy glucose molecules are broken down into carbon dioxide and water.






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cellular_respiration_3-58b9a5415f9b58af5c839e04.jpg)